
Another common theme is a single, large, fixed deduction. Charitable deductions and home mortgage interest are the most discussed examples of deductions that would be retained, as these deductions are popular with voters and are often used.

Modified flat taxes have been proposed which would allow deductions for a very few items, while still eliminating the vast majority of existing deductions. The difference between a true flat tax and a marginally flat tax can be reconciled by recognizing that the latter simply excludes certain types of income from being defined as taxable income hence, both kinds of tax are flat on taxable income.įlat tax with limited deductions Such a tax is said to be marginally flat above that point. Where deductions are allowed, a 'flat tax' is a progressive tax with the special characteristic that, above the maximum deduction, the marginal rate on all further income is constant.

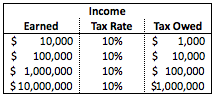
The defining characteristic is the existence of only one tax rate other than zero, as opposed to multiple non-zero rates that vary depending on the amount subject to taxation.Ī flat tax system is usually discussed in the context of an income tax, where progressivity is common, but it may also apply to taxes on consumption, property or transfers.įlat tax proposals differ in how the subject of the tax is defined.Ī true flat-rate tax is a system of taxation where one tax rate is applied to all personal income with no deductions. There are various tax systems that are labeled "flat tax" even though they are significantly different. Implementations are often progressive due to exemptions, or regressive in case of a maximum taxable amount. It is not necessarily a fully proportional tax. A flat tax (short for flat-rate tax) is a tax with a single rate on the taxable amount, after accounting for any deductions or exemptions from the tax base.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
